Turing RK1 is 2x faster, 1.8x pricier than Pi 5
I've long been a fan of Pi clusters. It may be an irrational hobby, building tiny underpowered SBC clusters I can fit in my backpack, but it is a fun hobby.
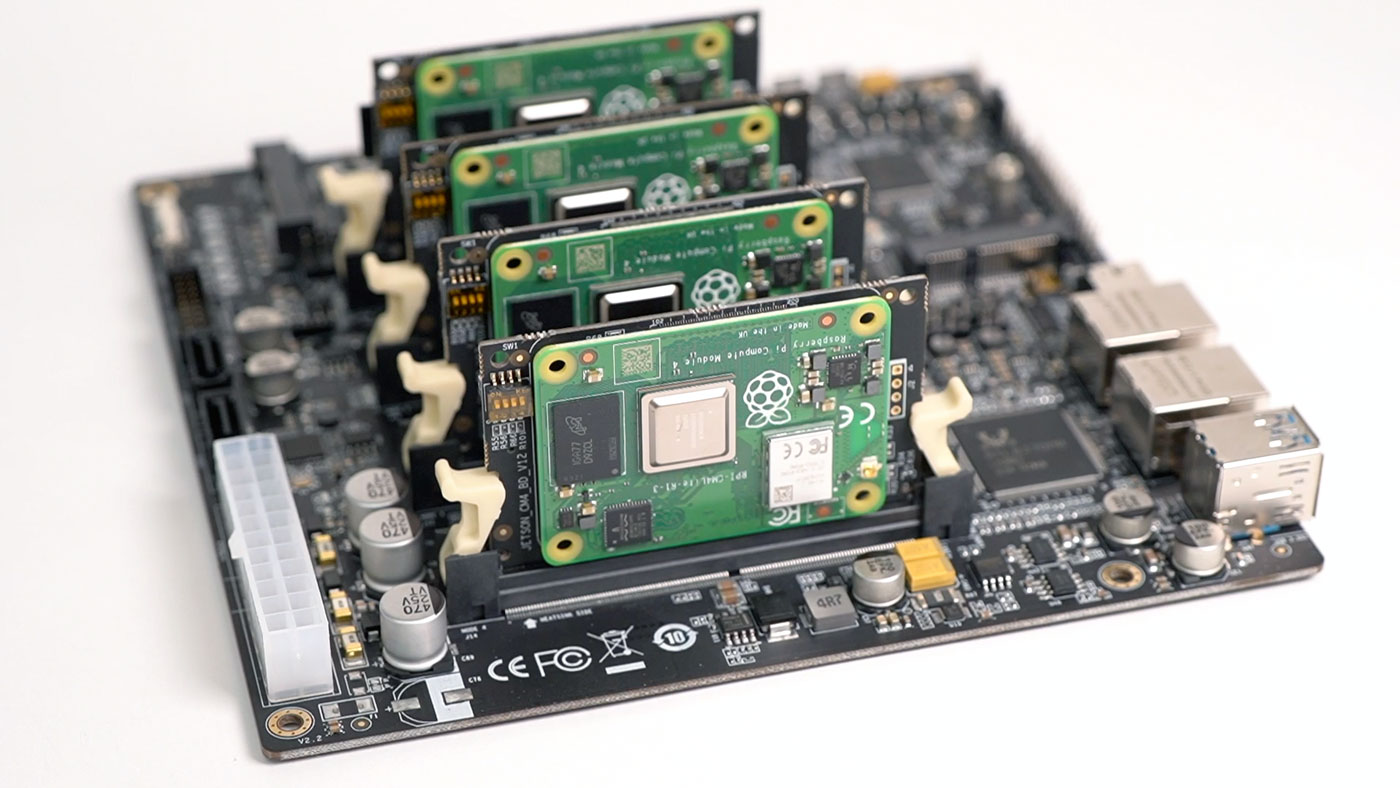
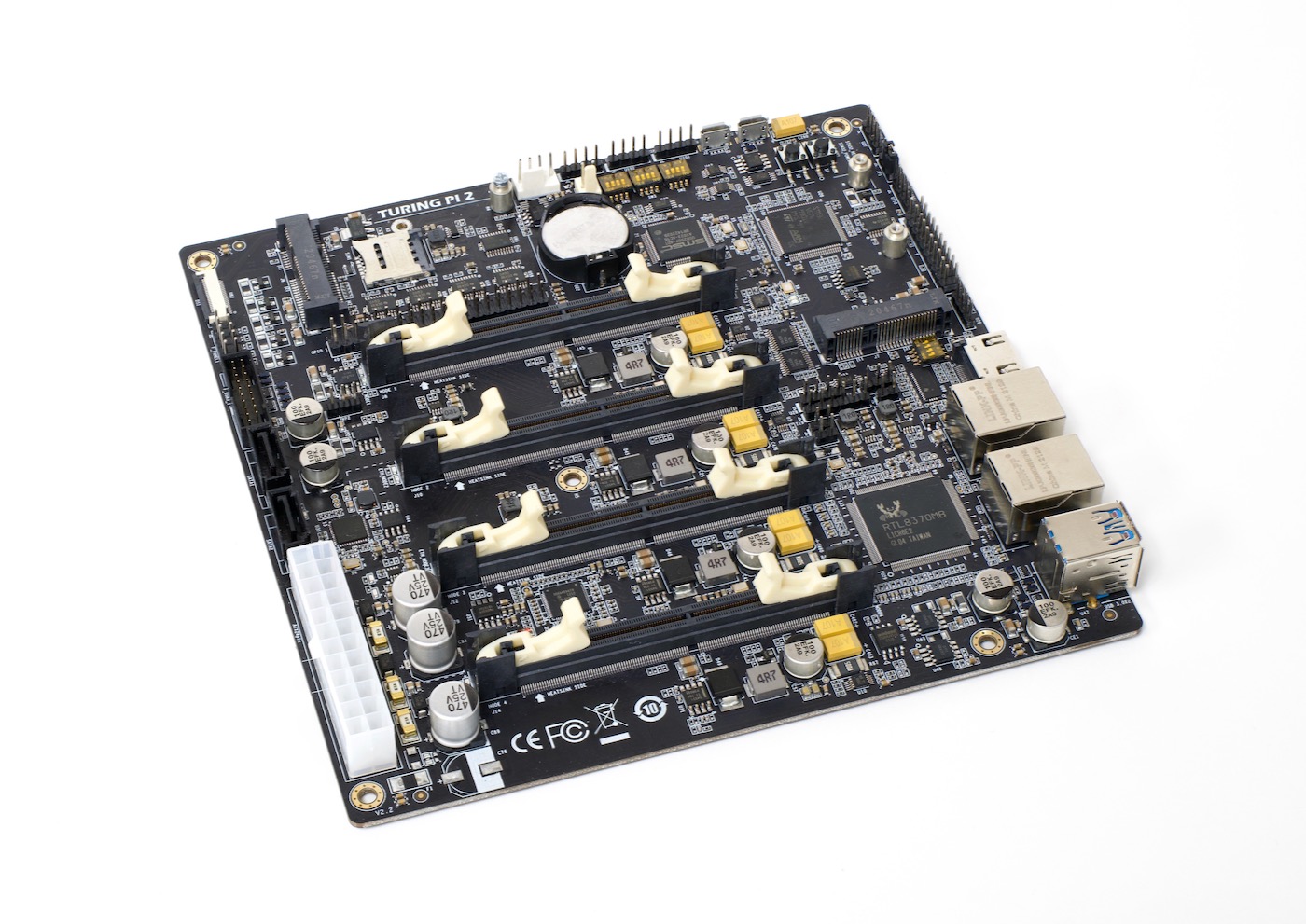
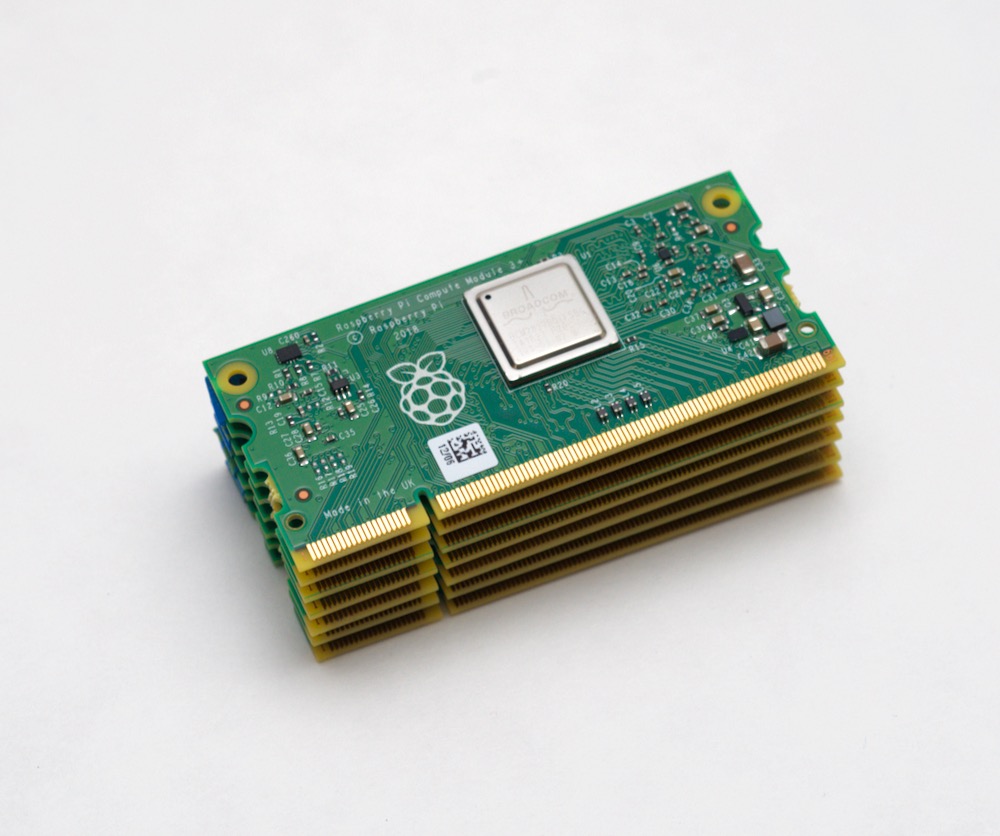
And a couple years ago, the 'cluster on a board' concept reached its pinnacle with the Turing Pi 2, which I tested using four Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4's.
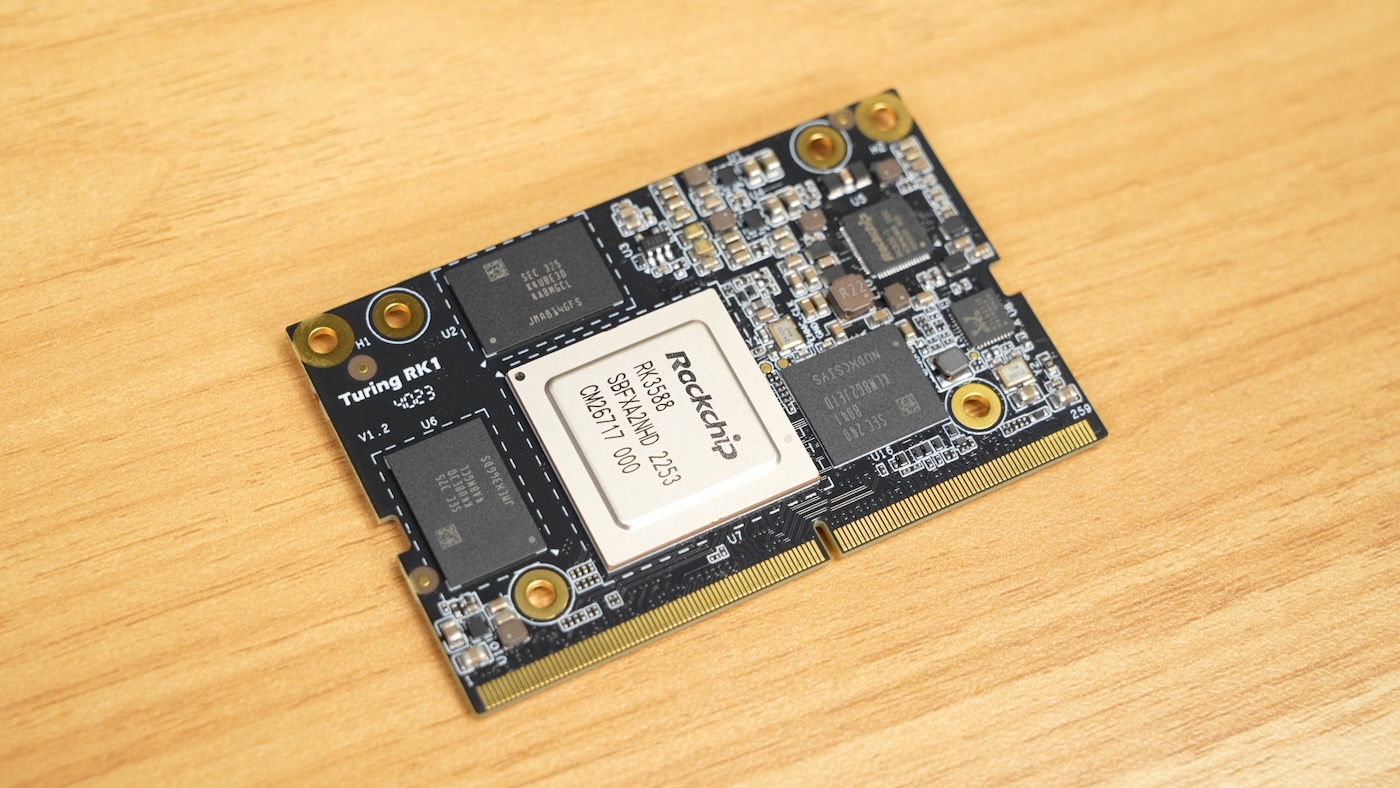
Because Pi availability was nonexistent for a few years, many hardware companies started building their own substitutes—and Turing Pi was no exception. They started designing a new SoM (System on Module) compatible with their Turing Pi 2 board (which uses an Nvidia Jetson-compatible pinout), and the result is the RK1: